COVID-19 and the paradigm of fantasy-based medicine
For a drug to be considered effective against a disease, it needs to undergo research with methodological rigor and that can attest to real benefits and risks
07/04/2021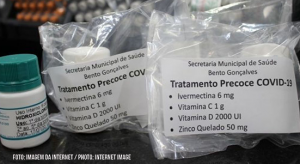
To date, none of the drugs used indiscriminately against COVID-19 that have been subjected to this level of scrutiny have been approved by scientists to prevent or treat mild cases of the disease
Brazilian medical and scientific communities are emphatic in repudiating the supposed early treatment proposed by the federal government against the new coronavirus, which involves drugs with no proven efficacy. According to the Federal Council of Pharmacy (CFF), there is no scientific evidence that the drugs that normally make up the so-called COVID kit offer any benefit in preventing or treating the disease. The Brazilian Medical Association (AMB) even recommended banning the drugs that make up the kit. In a letter released on March 23, the AMB reaffirmed that chloroquine, hydroxychloroquine, ivermectin and azithromycin have no proven scientific efficacy in the treatment or prevention of COVID-19 at any stage of the disease. However, even with the ineffectiveness of drugs used in early treatment, the president of the Federal Council of Medicine (CFM), Mauro Ribeiro, said on March 25 that the agency will not review the endorsement given to doctors for the use of drugs. The use of this type of treatment was discouraged by the World Health Organization (WHO).
Recently lawyers, doctors and civil society representatives “signed a representation” taken to the Federal Public Prosecutors Office (MPF) with questions about the performance of the Federal Council of Medicine during the pandemic in Brazil. According to the document, the class entity was silent in failing to act against the spread of the false idea of the existence of effective early treatment against COVID-19, represented by the indiscriminate use of drugs without proven efficacy against the disease. The representation requests that a civil investigation be initiated to ascertain the civil, administrative and/or criminal liability of the CFM Board.
CFMs omission to publicly manifest a clear scientific position with a view to discouraging the spread of misleading practices and information (a) in the medical prescription of an alleged early treatment against COVID-19, which has no scientific evidence, is configured of effectiveness and for which the recommendation of compassionate use is no longer justified, since there are effective alternatives and (b) in the dissemination of false health security, which would allow the population to abandon the practices of proven efficacy, notably the use of masks, asepsis of hands and points of contact and social isolation. In view of the omission of a clear scientific recommendation by the competent body, a considerable part of society has been guided by the false belief that there is an early treatment that, in reality, does not present scientific and reliable evidence of being effective. Furthermore, this false belief in a treatment causes noncompliance with the measures that are proven to prevent the spread of COVID-19. And the failure of the effective measures by a part of society exposes the entire population of the country to contamination”, emphasizes the document.
False security that can lead to death
The sale of drugs with no proven effectiveness against COVID-19 has skyrocketed. Only in the case of hydroxychloroquine, the total more than doubled, from 963 thousand in 2019 to 2 million units in 2020, according to a survey obtained exclusively by G1 from the Federal Pharmacy Council. Figures from the entity also show that the total units sold of ivermectin, for example, rose 557% in 2020 compared to 2019, with December being the record-breaking month for sales of the drug.
Heads of Brazilian Intensive Care Units (ICUs) and intensive care physicians have again opposed the use of the COVID kit in the so-called early treatment. Professionals heard in a BBC Brazil report said that drugs that do not have proven efficacy are not only unable to help prevent serious cases of the disease, but the use of drugs unnecessarily worsens the clinical conditions of critically ill patients and may make it difficult to survive intubation cases or more serious forms of COVID-19.
According to a report by Estadão, the use of ineffective drugs, present in the COVID kit, put five patients on the liver transplant line in São Paulo. There is also an investigation into the death of at least three patients due to drug-induced hepatitis. Also according to the report, the kit may also have caused bleeding, kidney failure and arrhythmias in patients who used the drugs. According to doctors, the deaths occurred due to acute liver disease, and not to conditions associated with contamination by the new coronavirus. In some cases, liver enzymes showed changes 30 to 40 times greater than the ideal, directly indicating a picture of drug hepatitis caused by the indiscriminate use of drugs.
Referral hospital doctors heard by BBC News Brasilclaim that the defense and use of the COVID kit contribute in different ways to increase deaths in the country. According to the report, the kit also kills indirectly, by slowing the populations demand for care, absorbing public money that could buy medicines for intubation, and by mastering the message to combat the pandemic, while national care protocols were not even adopted. Among the effects of the late demand for care is intubation. The greatest concern of intensive care physicians is the side effect of these medications on patients who progress to the severe form of the disease and who already have the functioning of vital organs compromised.
While Paraná continues with an explosion in the number of cases and a record of deaths, a group of doctors and businesspeople from Curitiba began to publicly defend early treatment as a way to relieve hospitals and reduce the level of deaths. One of the actions that drew the most attention was the installation of ten billboards around the city, funded by the group “Médicos pela Vida”, which brings together professionals from different medical specialties and also people from other areas. The advertising, which featured the image of a professional on the front line facing the pandemic highlighted in one corner of the piece, highlighted the phrase: do not give COVID-19 a chance. Early treatment saves lives. The piece was removed by order of the City Hall of Curitiba, in a decision that served the letter of the Public Prosecutors Office for the Protection of Public Health of Curitiba, of the Public Ministry (MP-PR).
A preliminary study entitled “SARS-CoV-2 Seroprevalence and Associated Factors study in Manaus, Brazil: Baseline Results from the DETECTCoV-19 Cohort Study” developed by Fiocruz Amazonia (Fiocruz/AM) and the Federal University of Amazonas (UFAM) concluded that people who had preventive treatment for COVID-19, using drugs without scientific proof, had a higher rate of infection compared to those who did not use them, in Manaus. Given the data, the researchers associate this reality to the fact that people who use these drugs, such as ivermectin, end up neglecting the safest ways to avoid the disease, including physical isolation and the use of a mask. Of the survey participants, 38.64% of those who tested positive had taken some medication to prevent contamination of the disease. While among those who did not take anything, the infection rate was 25.99%.
The first Brazilian study to “evaluate adverse drug reactions (ADRs) in patients with COVID-19” revealed that the drugs most involved in the reactions were hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine and azithromycin. The research described 631 ADRs in 402 patients from March 1 2020 to August 15 2020. The main drugs suspected of causing the reactions were hydroxychloroquine (59.5%), azithromycin (9.8%) and chloroquine (5.2%). The work analyzed records of the Pharmacovigilance System of the National Health Surveillance Agency (Anvisa) at the peak of the pandemic. During the period, 631 reactions were reported in more than 400 patients, most of them (and the most serious) caused by chloroquine and azithromycin. Among the drugs consumed, 748 (60%) were considered concomitant, 17 (1.4%) as drug interaction with other drugs and 482 (38.6%) suspected of causing the reactions. Among the suspected or interacting drugs (n = 499), the most frequent (79.7%) were hydroxychloroquine (59.5%), azithromycin (9.8%), chloroquine (5.2%) and ceftriaxone with 3.2%.
Side effects and adverse reactions of the COVID kit
Hydroxychloroquine: medication normally used in patients with lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, photosensitive diseases and malaria. The use can cause abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, acute liver damage, myopathy, vertigo, extrapyramidal reactions, seizures (especially in patients with a previous history), tachycardia, prolongation of the QT interval, among many other adverse effects, among many others, where the cardiovascular are those that raise most concerns.
Ivermectin: dewormer used to combat worms, lice and ticks. The use can cause hepatitis, diarrhea, abdominal pain, anorexia, constipation and vomiting, fever, tachycardia, headache, dizziness, drowsiness, dizziness and tremor, swelling in the limbs (arms, hands, legs and feet), hypotension, in addition to itching and rashes.
Azithromycin: an antibiotic that, according to doctors, should only be used in case of bacterial infection, not to prevent a virus. The most common side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, loose stools, abdominal discomfort, constipation or diarrhea and gas. In addition, dizziness, drowsiness and loss of appetite may occur.
Nitazoxanide: it is an antiparasitic. The use can cause nausea, diarrhea, vomiting and abdominal pain, headache, allergic reaction, tachycardia, changes in eye color, urine and sperm; and also redness, itching and rashes on the skin.
Vitamin D: can cause dry mouth, headache, loss of appetite, nausea, fatigue, feeling of weakness, muscle pain, itching and weight loss. Excessive consumption can also cause constipation, muscle weakness, vomiting, irritability and dehydration. In addition, excess vitamin D, for prolonged periods, can result in endocrine and metabolic changes, such as proteinuria, renal dysfunction, hypertension, arrhythmias, worsening of gastrointestinal symptoms, pancreatitis, psychosis, reduced HDL levels and increased LDL levels.
Vitamin C: administration of high doses, for a prolonged period, can cause rebound scurvy, digestive disorders, erythema, headache, increased diuresis and lithiasis in patients with renal failure and in those predisposed to kidney stones. In addition, it is important to remember that all these drugs have contraindications and can alter the effects of other drugs already in use by the patient.
In a country where a significant portion of the population prefers to risk their lives believing they are protected by some pills, we seek an answer to the question: whether the early treatment advocated by the federal government is a way out, which explains the devastation imposed by COVID-19 on so many Brazilian cities?