Case report: frequent clinical complications in the Northeast region of Brazil
Main differential diagnosis is with cases of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-infected patients
08/09/2020
Patient has been diagnosed with HIV infection since 2008, without undertaking antiretroviral therapy. Laboratory tests revealed pancytopenia, increased lactic dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase, transaminases (TGO>TGP) and c-reactive protein. The last viral load is 2,575,096 copies, CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes count of 11 and 59 respectively.
Patient RDC, 37 years old, male, transgender woman, sex worker, black, crack cocaine user, born in Macau-RN, arriving Natal-RN, has been diagnosed with HIV infection since 2008, without using antiretroviral therapy. A month ago, she started a daily high, intermittent fever ranging from 38.5 to 40ºC when measured, which yields in lysis, without chills and weight loss of about 10 kg.
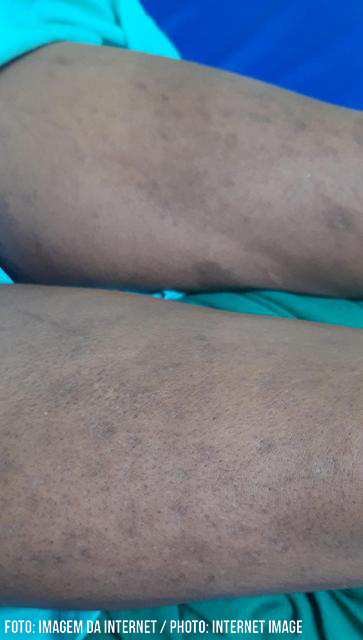
When admitted to the infectious diseases emergency room at the Hospital Giselda Trigueiro/Natal/RN in July 2020, she was feverish, dehydrated 1+/4+, pale 2+/4+, vigilant, anicteric, acyanotic with brown spots on her thighs, legs and torso.
Figure 1: Photograph of the patients skin showing disseminated maculopapular lesions. The lesions are symmetrical, bilateral, painless with about 10mm in the largest diameter.
The examination of the respiratory and cardiovascular system had normal results. In the evaluation of the abdomen, painful hepatomegaly was found with hepatimetry 4 cm from the right costal margin, without splenomegaly.
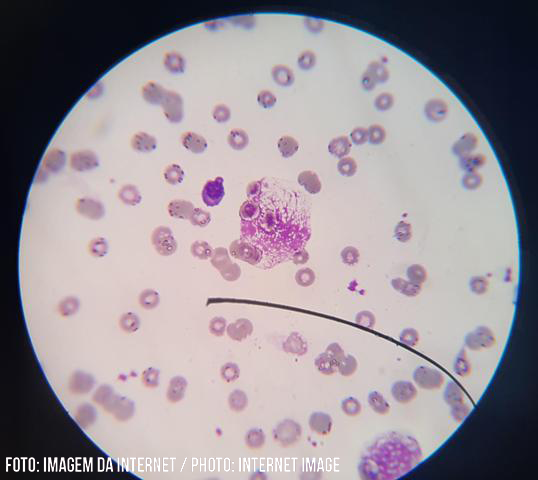
The Laboratory tests revealed pancytopenia, increased lactic dehydrogenase, alkaline phosphatase, transaminases (TGO>TGP) and c-reactive protein. The last viral load is 2,575,096 copies, CD4+ and CD8+ lymphocytes count of 11 and 59 respectively. Bone marrow aspirate was then performed on the iliac crest, which after staining revealed oval structures with birefringent capsule compatible with intra and extra-cellular histoplasma sp.
Figure 2: Examination of the patients bone marrow, revealing the presence of histoplasma sp in the bone marrow aspirate. Differential diagnosis with leishmania should be made. The dimensions are similar, however in leishmania the presence of the kinetoplast is observed, absent in this case.
This case represents a frequent clinical complication in the Northeast region of Brazil and is important because the main differential diagnosis is with cases of visceral leishmaniasis in HIV-infected patients.
In this case, prolonged fever, hepatomegaly, skin lesions in combination with pancytopenia are very suggestive of disseminated histoplasmosis. This infection, when present in patients with a significant drop in the CD4+ count, may represent the possibility of progression to death and requires rapid diagnosis as well as drug intervention. In some cases, the investigation of the histoplasma antigen may be performed, but the examination of the spinal fluid is essential to differentiate histoplasmosis from visceral leishmaniasis.
Participated in the elaboration of this case:
Professor Kleber Luz – Department of Infectious Diseases, Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte.
Aline Raginini – Resident Physician of the Second Year of Infectious Diseases at the Federal University of Rio Grande do Norte.